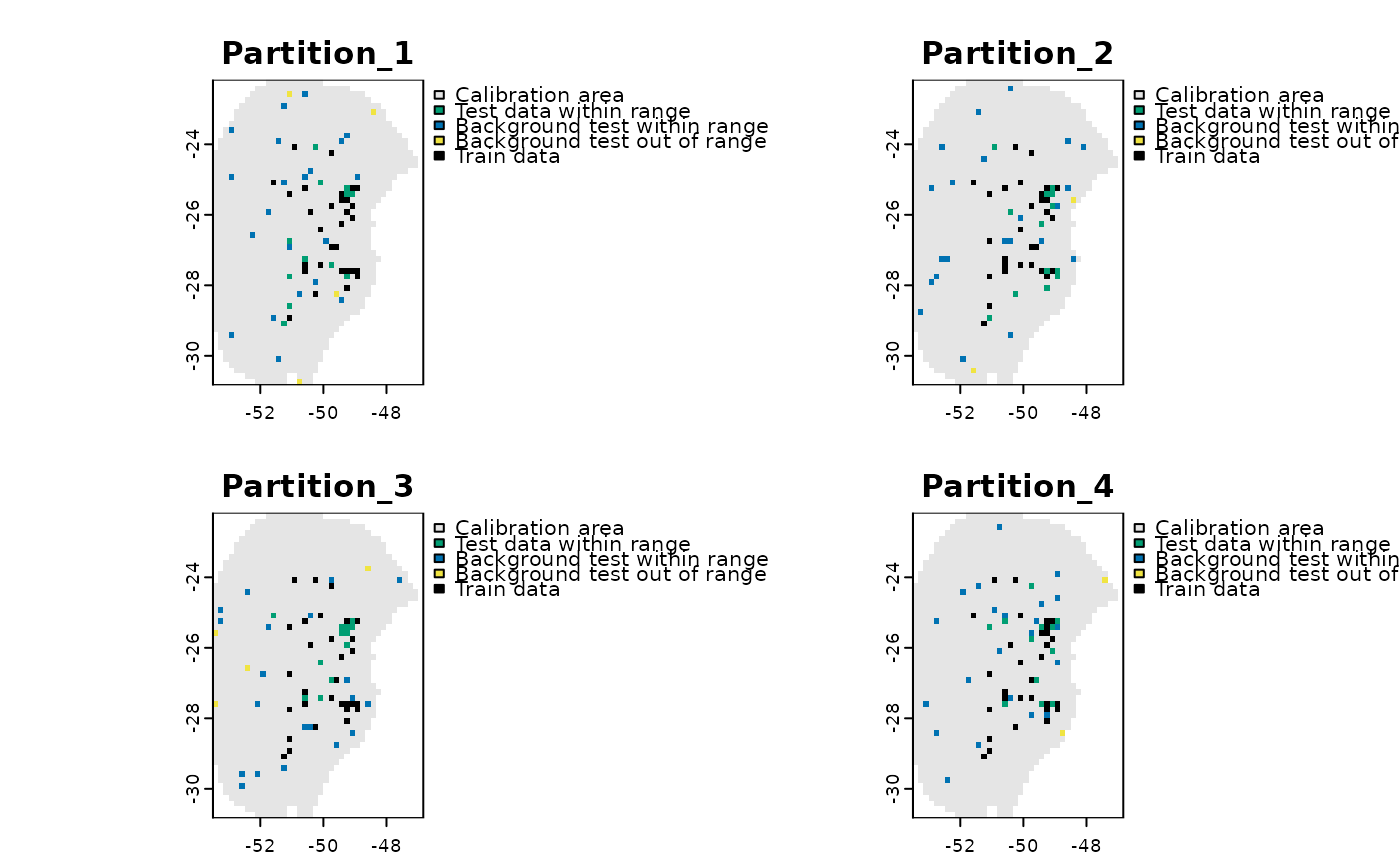
Analysis of extrapolation risks in partitions using the MOP metric
Source:R/explore_partition_extrapolation.R
explore_partition_extrapolation.RdThis function calculates environmental dissimilarities and identifies non-analogous conditions by comparing the training data against the test data for each partition, using the MOP (Mobility-Oriented Parity) metric.
Usage
explore_partition_extrapolation(data, include_train_background = TRUE,
include_test_background = FALSE,
variables = NULL,
mop_type = "detailed",
calculate_distance = TRUE,
where_distance = "all",
return_raster_result = TRUE,
raster_variables = NULL,
progress_bar = FALSE, ...)Arguments
- data
an object of class
prepared_datareturned by theprepare_data()function.- include_train_background
(logical) whether to include the background points used in training to define the environmental range of the training data. If set to FALSE, only the environmental conditions of the training presence records will be considered. Default is TRUE, meaning both presence and background points are used.
- include_test_background
(logical) whether to compute MOP for both the test presence records and the background points not used during training. Default is FALSE, meaning MOP will be calculated only for the test presences.
- variables
(character) names of the variables to be used in the MOP calculation. Default is NULL, meaning all variables in
datawill be used.- mop_type
(character) type of MOP analysis to be performed. Options available are "basic", "simple" and "detailed". Default is 'simples'. See
projection_mop() for more details.- calculate_distance
(logical) whether to calculate distances (dissimilarities) between train and test data. Default is TRUE.
- where_distance
(character) specifies which values in train data should be used to calculate distances. Options are: "in_range" (only conditions within the train range), "out_range" (only conditions outside the train range), and "all" (all conditions). Default is "all".
- return_raster_result
(logical) whether to return a
SpatRastershowing the spatial distribution of test data that falls within and outside the range of the training data. Default is TRUE.- raster_variables
a
SpatRasterobject representing the predictor variables used to calibrate the models. Preferably the same object used inprepare_data. Only used ifreturn_raster_result = TRUE.- progress_bar
(logical) whether to display a progress bar during processing. Default is FALSE.
- ...
additional arguments passed to
mop().
Value
A data.frame containing:
MOP distances (if
calculate_distance = TRUE);an indicator of whether environmental conditions at each test record fall within the training range;
the number of variables outside the training range;
the names of variables with values lower or higher than the training range;
if the
prepared_dataobject includes categorical variables, it will also contain columns indicating which values in the testing data were not present in the training data.
If return_raster_result = TRUE, it also returns a SpatRaster showing the
spatial distribution of test data that falls within and outside the range of
the training data.
Examples
#Prepare data
# Import occurrences
data(occ_data, package = "kuenm2")
# Import raster layers
var <- terra::rast(system.file("extdata", "Current_variables.tif",
package = "kuenm2"))
# Prepare data for maxnet model
sp_swd <- prepare_data(algorithm = "maxnet", occ = occ_data,
x = "x", y = "y",
raster_variables = var,
species = occ_data[1, 1],
n_background = 100,
categorical_variables = "SoilType",
features = c("l", "lq"),
r_multiplier = 1,
partition_method = "kfolds")
#> Warning: 3 rows were excluded from database because NAs were found.
# Analysis of extrapolation risks in partitions
res <- explore_partition_extrapolation(data = sp_swd,
raster_variables = var,
include_test_background = TRUE)
#Plot spatial spatial distribution of test data
terra::plot(res$Spatial_results)